How Do Infant/Toddler Programs Support School Readiness?
All Head Start agencies serving infants and toddlers must establish program goals for improving the school readiness of participating children; and take steps to achieve these goals (45 CFR XIII 1307.3 (b)(1)&(2), as amended). The Office of Head Start has developed resources and materials to support programs in developing and implementing school readiness goals for infants and toddlers, based on the following foundations and principles. Note: These resources are under review.
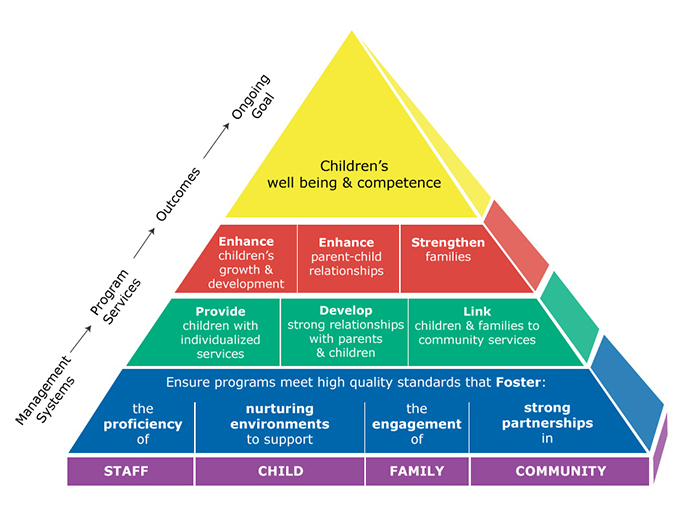
REVISED Framework for Programs Serving Infants and Toddlers and Their Families
- This conceptual framework provides a guide for programs to develop and implement supports for the healthy growth and development of expectant families, babies, and toddlers. Strong management systems provide the foundation for implementing comprehensive child development and family support services that lead to positive outcomes for very young children and their families.
- Through the implementation of continuous and comprehensive child development and family support services, program staff builds trusting and respectful relationships with families that integrate their values, beliefs, and caregiving practices. Trust and attachment are the context for learning and development in the five essential domains – physical and health, social and emotional, approaches to learning, cognition and general learning, and language and literacy.
- Fostering healthy development and secure attachment begins prenatally and continues to influence the developmental competence of very young children throughout their first years. Infants’ and toddlers’ well-being and competence in the five essential domains is developed in the context of trusting relationships. Ensuring positive relationships through nurturing experiences during the earliest years supports children’s developmental competence throughout their preschool and school years.
- Go to Research to Practice: Program Performance Measures for Head Start Programs Serving Infants and Toddlers [PDF, 225KB] and The Head Start Parent, Family, and Community Engagement Framework: Promoting Family Engagement and School Readiness, from Prenatal to Age 8 for more information.
Framework for Programs Serving Infants and Toddlers and Their Families
Head Start Approach to School Readiness – Full Text
School Readiness Goals for Infants and Toddlers
Agencies need to consider infant and toddler developmental needs when implementing the Four Action Steps to set and achieve appropriate school readiness goals for this age group:
- Establish goals for improving school readiness across the five essential domains: language and literacy, cognition and general knowledge, approaches to learning, physical development and health, and social and emotional development. Select this link for Program Level School Readiness Goals for Early Childhood Programs: Examples from the National Center on Early Childhood Development, Teaching, and Learning (NCECDTL).
- Create and implement an action plan for achieving the established school readiness goals;
- Assess child progress on an ongoing basis and aggregate and analyze data at multiple times throughout the year; and
- Examine data for patterns of progress for groups of children in order to revise, or develop and implement, plans for program improvement.
Providing a Foundation for School Readiness
The Head Start Act of 2007 requires that programs serve infants, toddlers, and their families by providing … "early, continuous, intensive, and comprehensive child development and family support services that will enhance the physical, social, emotional, and intellectual development of participating children" (Sec.645A (b)(1), 2007). How does this relate to improving school readiness for infants and toddlers?
Improving school readiness for infants and toddlers means providing a secure foundation for child development and early learning across domains that ensures children enter preschool, and eventually school, ready to succeed. The large body of research on brain development and how babies learn clearly demonstrates the importance of secure attachments with adults as critical to babies’ overall development.
Below are considerations for a program structure and design to support the delivery of child-focused, family- centered services that promote infant/toddler development and early learning.
Implementing High-Quality Programs for Infants, Toddlers and Families
When implementing appropriate services across program options and settings that support achievement toward school readiness goals for infants and toddlers, consider:
- Is one primary caregiver assigned to each child in center-based Early Head Start programs? Is there one home visitor assigned long term in the home-based program option? Are there limited transitions within the day/week/month/year to ensure continuity of care?
- Do infants and toddlers and their families feel safe and secure within their program setting? Do staff use responsive caregiving practices to engage them? How are staff supported in an ongoing way to develop and foster close and trusting relationships among families, children, and colleagues?
- What curriculum is used? Is it rooted in the concept of learning through relationships and routines? Does it support developmental progress in school readiness goals across the five essential domains? What do group and individualized routines look like? Are routines based upon individual needs and preferences? How are staff supported to implement nurturing care routines and play experiences to intentionally support development and learning? How are families engaged "as the child’s first and primary teacher?"
- Are there written plans for individual children as well as for groups of children? Do the plans reflect developmental milestones for each child and progress in reaching them? How are families involved in determining developmental goals? Do plans and daily care practices include family care practices and routines, as best as possible, to implement continuity of care?
- Is the environment rich with language so that babies hear words and language describing the array of experiences throughout the day? Do developing toddlers find adults who listen and understand their own budding expressions? How are staff and families supported in using a variety of conversational styles to foster emerging concepts and cognitive learning?
- Is there a process of ongoing assessment that includes a valid and reliable instrument, observations of staff and family, and anecdotal records? How does planning include all staff and family members caring for the child? How does it document the adaptation of curricular goals based on baby/toddler progress across all domains?
- Is there a systematic process to look for patterns of progress and outcomes in groups of infants and toddlers? How is this information used to enhance program performance and design so all children succeed?
Resources on School Readiness for Infants and Toddlers
EHS Podcast: A Quick Look: Recent EHS NRC Resources to Assist you in Thinking About School Readiness for Infants and Toddlers. HHS/ACF/OHS/EHSNRC. 2013. English. Streaming Video. 00:07:28.
Family Engagement and Ongoing Child Assessment. HHS/ACF/OHS. 2011.
Guide to School Readiness Goals. HHS/ACF/OHS. 2011.
Head Start Act, as amended December 12, 2007, Sec. 645A describes Early Head Start Programs as providing:
- "Family-centered services for low-income families with very young children designed to promote the development of the children, and to enable their parents to fulfill their roles as parents and to move toward self-sufficiency" [Sec. 645A (a)].
- "Either directly or through referral, early, continuous, intensive, and comprehensive child development and family support services that will enhance the physical, social, emotional, and intellectual development of participating children" [Sec.645A (b)(1)].
Head Start and Early Head Start School Readiness Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs). HHS/ACF/OHS. March 2012.
Head Start Parent, Family, and Community Engagement Framework: Promoting Family Engagement and School Readiness, from Prenatal to Age 8. HHS/ACF/OHS. 2011.
Healthy Start, Grow Smart Series: Prepare My Child for School. DOA/ED/HHS. 2002.
News You Can Use: Approaches Toward Learning—Foundations of School Readiness Part 1 (Aug. 2012). HHS/ACF/OHS/EHSNRC. 2012.
News You Can Use: Approaches Toward Learning—Foundations of School Readiness Part 2 (Aug. 2012). HHS/ACF/OHS/EHSNRC. 2012.
News You Can Use: Approaches Toward Learning—Foundations of School Readiness Part 3 (Aug. 2012). HHS/ACF/OHS/EHSNRC. 2012.
News You Can Use: Early Experiences Build the Brain—Foundations of School Readiness (Oct. 2012). HHS/ACF/OHS/EHSNRC. 2012.
News You Can Use: Foundations of School Readiness: Language and Literacy (July 2013). HHS/ACF/OHS/EHSNRC. 2013.
Program Level School Readiness Goals for Early Childhood Programs: Examples from the National Center on Early Childhood Development, Teaching, and Learning (NCECDTL). HHS/ACF/OHS/NCECDTL. 2016.
Research to Practice: Program Performance Measures for Head Start Programs Serving Infants and Toddlers [PDF, 224.72KB]. HHS/ACF/OPRE. April 2006.
Resources for Measuring Services and Outcomes in Head Start Programs Serving Infants and Toddlers. HHS/ACF/OPRE. Revised 2011.
School Readiness Action Steps for Infants and Toddlers. HHS/ACF/OHS/EHSNRC. 2012. Available in Spanish.
TA Paper No. 6: Foundations to School Readiness for Infants and Toddlers: Fostering Developmental Competence in the Earliest Years. HHS/ACF/ACYF/HSB. 2003.
Last Updated: September 18, 2021